Sustainability is a big, relevant topic that concerns many people. It is not only about our own sustainable actions, but also about the design of sustainable industry. This therefore also applies to the aluminium industry. Because many things in everyday life depend massively on aluminium.
Aluminium is already making a major impact on reducing CO2 levels. For example, aluminium is used as a light metal in the construction of wind turbines or solar panels and therefore makes an important contribution to CO2 reduction. However, a lot of energy is also needed within the value-added process of aluminium, which increases the emission values.
New report provides information on approaches
The International Aluminium Institute (IAI) has published a new report in order to be able to evaluate the emission generation within the aluminium industry and to develop solutions. This report shows three central pathways to reduce the generation of greenhouse gases to a minimum over the next 30 years. First of all, a working group was founded to collect the necessary data.
This resulted in a data set from over 15 years. The data allows conclusions on the emission levels of all production steps and helps to identify processes with high greenhouse gas production. “This is the most comprehensive, detailed and up-to-date dataset that exists not just for aluminum but also any material today” says Miles Prosser, Secretary General of the IAI. One thing becomes unmistakably clear: massive investments will be needed to reduce emission levels despite rising demand for aluminium.
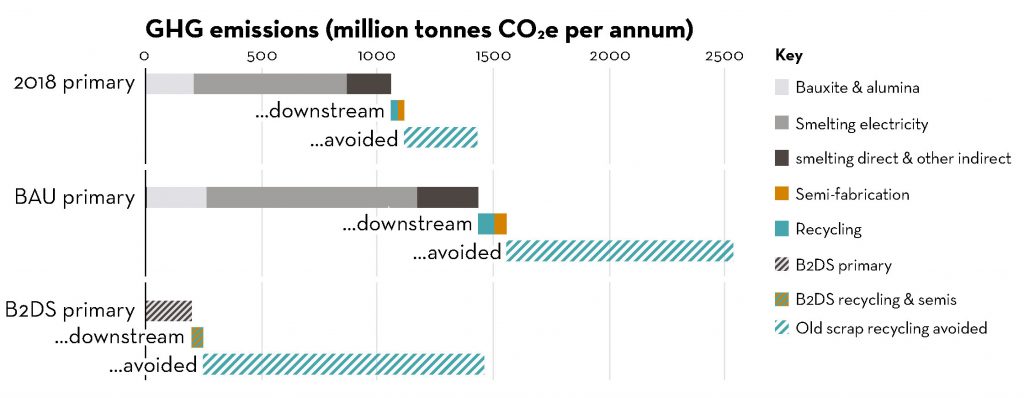
Three ways to reduce emissions
Based on this data set, the IAI working group developed three important ways to sustainably reduce greenhouse gas production in the aluminium industry. All three aspects have been largely responsible for the emission levels of the value creation process so far.
1 – Carbon-free electricity production
Electricity consumption is one of the biggest drivers of emissions, accounting for about 60% of CO2 emissions. A large part of this electricity consumption is generated in the aluminium smelting process. Most emissions could therefore already be avoided with carbon-free electricity.
2 – Direct emissions
Under direct emissions, the working group summarises those emissions that occur during combustion processes. This concerns, for example, the transport or storage of aluminium. These direct emissions also account for about 15 percent of total emissions. Electrification and renewable energies could therefore also reduce CO2 emissions here.
3 – Recycling and resource efficiency
So far, a large part of the aluminium is still primary aluminium. If a better recycling cycle were established, the demand for primary aluminium could be reduced by up to 20 per cent. This alone could avoid an increase in CO2 emissions of up to 300 million tonnes.
Sustainability is an essential challenge for the aluminium industry
The demand for aluminium continues to grow. But this is precisely why it is even more important for the aluminium industry to address the question of sustainable action. Today, aluminium as a material already helps to reduce emissions. But by focusing on some of the CO2 drivers within aluminium production, further massive savings could become possible. The recycling process and the savings in “non-clean energy” in the manufacturing process in particular offer a lot of savings potential.
Source: lightmetalage.com
